Organizations manage a broad spectrum of official documents, from internal memos and client proposals to compliance submissions and operational guidelines. Creating these documents often demands considerable time and attention to consistency, accuracy, and compliance with standards. Recent advances in generative AI offer new ways to simplify and accelerate this process. By using multiple AI agents working together through frameworks such as Microsoft’s Semantic Kernel combined with Azure OpenAI Service, companies can automate the creation, validation, and formatting of documents more effectively.
In this article, I’ll demonstrate a practical example of how AI-driven workflows can simplify and enhance document creation in an enterprise context.
We’ll combine both single-agent and multi-agent approaches for generating the document:
Models in Use:
- GPT-4o: Used for the multi-agent workflows, enabling self-correction, iterative execution, and adaptive decision-making for complex tasks.
- o3-mini: Handles single-agent operations with predefined parameters, suitable for scenarios where the context is fully known in advance.
Agent Orchestration Framework:
- Semantic Kernel (SK): Serves as the core orchestration framework.
Step-by-Step Document Processing:
- Markdown Drafting: Initial document generation in Markdown, allowing human-in-the-loop review.
- Validation & Refinement: Compliance checks are based on a predefined checklist, with the agent verifying one checklist item at a time. These findings can serve as the basis for the human-in-the-loop review step in Step 1, enabling feedback to flow back into the drafting process.
- DOCX Conversion: Markdown is transformed into a final Word document for formatting and final review before distribution.
Why a Multi-Agent Approach for Enterprise Documents?
- Accuracy: Different agents specialize in precise roles. This division of labor ensures each step is handled effectively.
- Consistency: By automating the drafting and reviewing steps, the system can maintain consistent tone, structure, and branding across large volumes of documents.
- Allows Human Oversight: Agents handle repetitive tasks and can raise warnings or questions for a human reviewer to address.
- Scale: In many large organizations, a single process (e.g. sending official notices to thousands of recipients) can be parallelized by spinning up more agent instances.

Overview of the Workflow
The example repository demonstrates how to produce a “Declaration of Commitment,” but these same patterns apply to countless enterprise document scenarios.
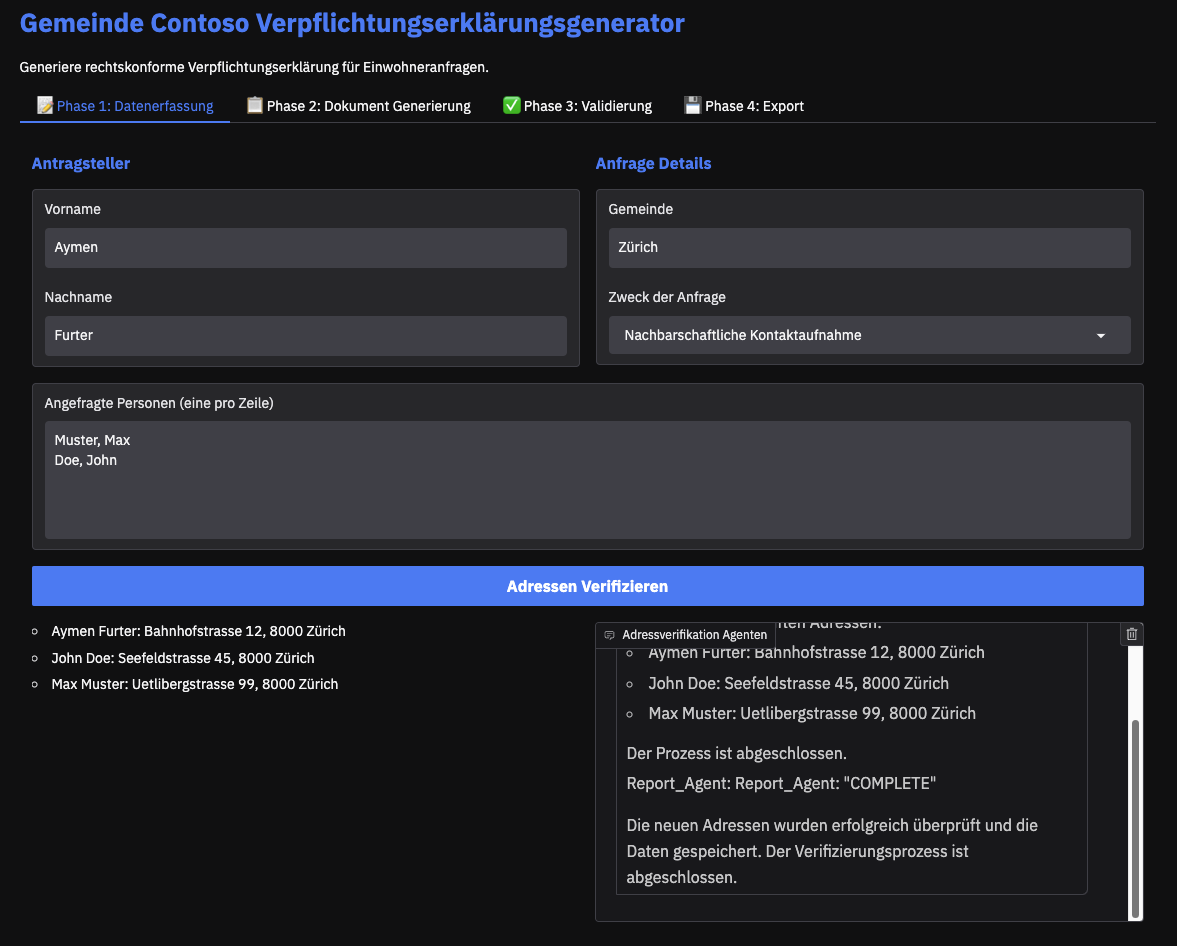
Phase 1: Data Collection
In this phase, specific data is retrieved in real-time via plugins connected directly to your backend systems or APIs. A dual-agent architecture using Semantic Kernel is employed: one agent fetches the required data (in the sample code below, this agent looks up address information for individuals relevant to the document being generated), while the second agent reports and stores the retrieved data for later use.
def create_address_agents(kernel: Kernel) -> Tuple[ChatCompletionAgent, ChatCompletionAgent]:
"""
Create and return the two specialized agents for address verification workflow
"""
# Define standard arguments
agent_args = KernelArguments(
settings=PromptExecutionSettings(
function_choice_behavior=FunctionChoiceBehavior.Auto(),
extension_data={}
)
)
# Create retriever agent for address lookups
retriever_agent = ChatCompletionAgent(
kernel=kernel,
service=kernel.get_service(),
name=RETRIEVER,
plugins=["address"],
instructions="""
Adressverifizierer via Address API:
1. Namen in "Vorname Nachname" Format konvertieren
2. API nutzen: address.search_person(name="Vorname Nachname", location="gemeinde")
3. Ergebnis formatieren:
...
"""
)
# Create report agent for collecting results
report_agent = ChatCompletionAgent(
kernel=kernel,
service=kernel.get_service(),
name=REPORT_AGENT,
plugins=["report"],
instructions="""
Sammle und speichere Adressverifizierungsergebnisse:
1. Überwache, ob alle Personen verifiziert wurden
2. "COMPLETE" ausgeben, wenn alle überprüft wurden
3. Speichere Daten strukturiert mit report.save_people_data(people_data)
"""
)
return (retriever_agent, report_agent)
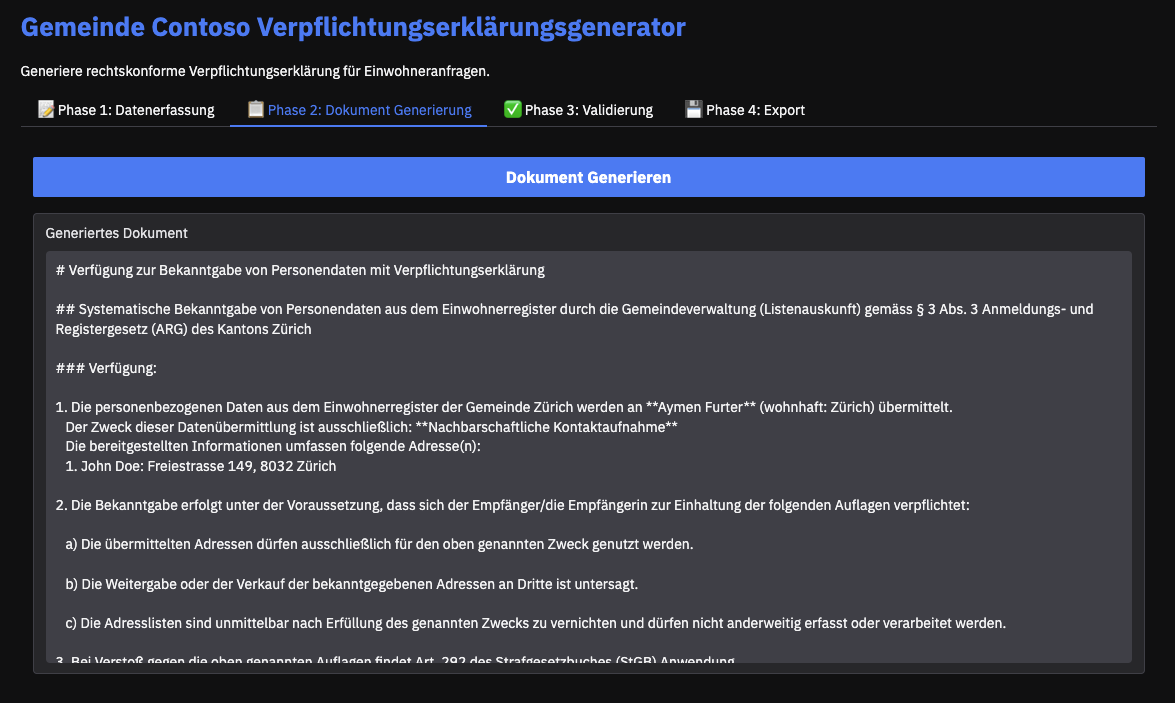
Phase 2: AI-Powered Document Generation (Markdown)
The collected data from Phase 1 is then combined with the markdown template to compile a detailed prompt. This prompt includes both the context (the collected data) and the markdown formatting structure required for the document. The prompt is then submitted to the a reasoning model (“o3-mini”). The LLM processes this input and returns an updated, draft of the document directly in markdown format.
async def generate_document(self, context: DocumentContext) -> str:
"""
Generate a document based on the provided context.
"""
# Build the prompt with placeholders
prompt = f"""
Du bist ein Experte für das Erstellen von behördlichen Dokumenten
...
VORLAGE:
{self.template}
"""
result = await self.kernel.invoke_prompt(
prompt=prompt,
settings=PromptExecutionSettings(
temperature=0.7,
top_p=1,
frequency_penalty=0.0,
presence_penalty=0.0
)
)
return str(result).strip()
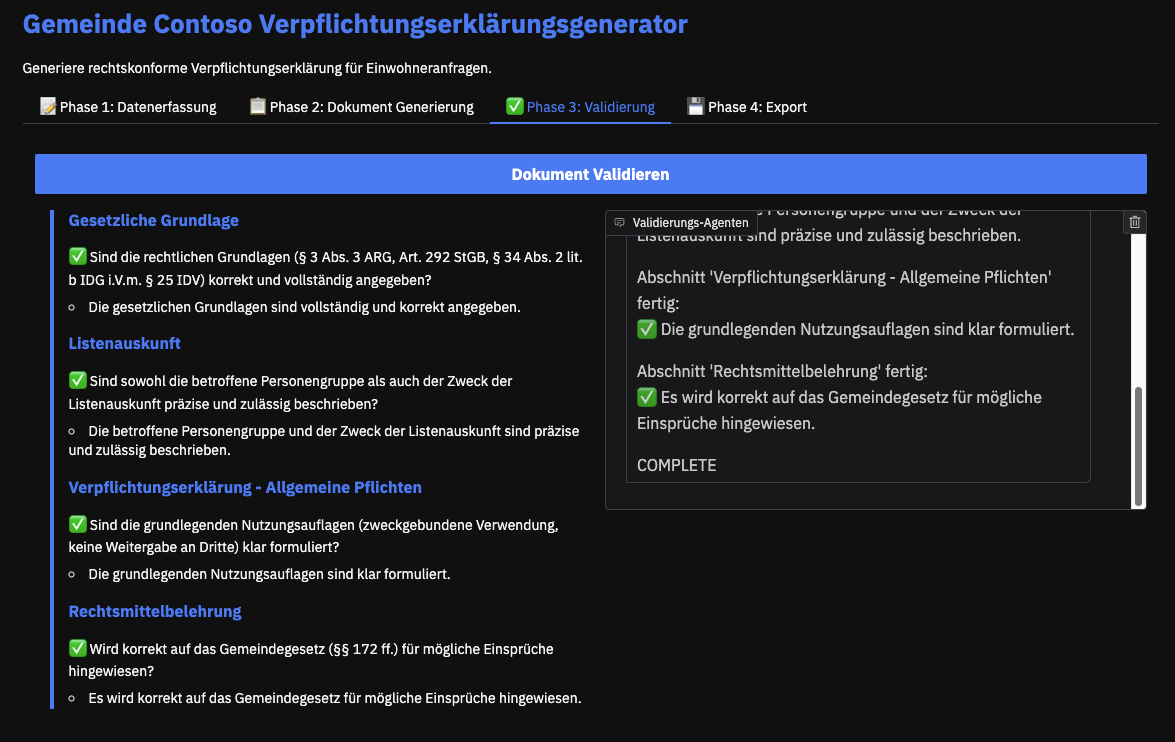
Phase 3: Validation (with Human in the Loop)
The drafted Markdown text is checked against a compliance checklist to ensure all legal references, disclaimers, required signatures, and other mandatory elements are included. This is achieved using another dual-agent setup: a Validator Agent reviews each checklist item, while a Reporter Agent monitors and determines when the validation process is complete. If any issues or inconsistencies are identified during validation, these are highlighted for human reviewers, who can then manually adjust the Markdown draft accordingly.
def create_validation_agents(kernel: Kernel) -> Tuple[ChatCompletionAgent, ChatCompletionAgent]:
"""
Create and return the two specialized agents for document validation workflow
"""
# Validator agent for checking compliance items
validator_agent = ChatCompletionAgent(
kernel=kernel,
service=kernel.get_service(),
name=VALIDATOR,
plugins=["compliance"],
instructions="""
Du bist ein Validator-Agent
...
1. Prüfe jeden Validierungspunkt
...
"""
)
# Compliance reporter agent for summarizing results
reporter_agent = ChatCompletionAgent(
kernel=kernel,
service=kernel.get_service(),
name=COMPLIANCE_REPORTER,
plugins=["compliance"],
instructions="""
Du bist ein Reporter-Agent
...
1. Überwache den Validierungsfortschritt
...
"""
)
return (validator_agent, reporter_agent)

Phase 4: DOCX Export
The validated Markdown content is converted into a .docx document using a predefined Word template. This is done using Pandoc, which applies specific formatting styles (including fonts, headers, and spacing) to generate the finalized document.
Adapting This Pattern to Your Needs
The demonstrated patterns and techniques can be generalized beyond this specific example to automate a wide range of enterprise document workflows:
- Corporate Actions: Automate the creation of shareholder notices, regulatory filings, and disclosures to ensure compliance and timely distribution.
- Public Sector Communication: Automate the drafting of official letters, notices, or regulatory documents, ensuring that updates and policies are communicated clearly and consistently.
- Customer Service Responses: Automate personalized responses for inquiries, ensuring consistent and compliant communication across various customer interactions.
By breaking down data gathering, AI drafting, compliance checks, and final output, you avoid many pitfalls of manual processes.
Final Thoughts
The way we compose customer communications is transforming. AI now streamlines every step of the process. If your team fights with manual document processes, I encourage you to explore the reference repository. Clone it, walk through the code, and experiment with adapting it to your use case. All relevant code samples are available in the repository at https://github.com/aymenfurter/ai-document-producer.